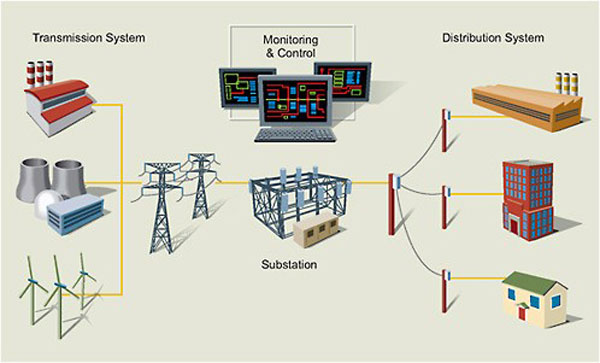
SCADA Training for Electric Utility T&D Systems. This comprehensive 12-Hour Live Online, Instructor-led training course is designed to provide you with an in-depth understanding of SCADA systems, their applications, and the essential skills required to successfully implement and maintain SCADA technology in the electric utility Transmission and Distribution (T&D) industry.
In today's fast-paced, increasingly interconnected world, the reliable and efficient operation of electric utility T&D systems is of paramount importance. SCADA systems play a crucial role in achieving this, enabling real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of the complex networks that form the backbone of our power grid. With the growing integration of renewable energy sources, distributed generation, and smart grid technologies, the importance of skilled professionals who understand SCADA systems in the T&D industry has never been greater.
This course is designed for engineers, technicians, operators, and other professionals who are involved in the planning, design, implementation, or maintenance of SCADA systems in the electric utility T&D industry. It is also suitable for those who seek a comprehensive understanding of the technology and its applications in this sector.
Throughout the course, you will gain hands-on experience with SCADA system components, communication technologies, and protocols, as well as practical insights into their application in substations, power distribution networks, and transmission networks. You will also learn about the critical aspect of cybersecurity, system maintenance, and troubleshooting.
By completing this SCADA training, you will be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to contribute to the success of your organization, ensuring the stability, efficiency, and security of our power grid. With the practical experience and industry-specific expertise gained in this course, you will be well-prepared to face the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of electric utility T&D systems.
Learning Outcomes
Upon successful completion of this SCADA Training for Electric Utility T&D Systems course, participants will be able to:
This course is designed for engineers, technicians, operators, and other professionals who are involved in the planning, design, implementation, or maintenance of SCADA systems in the electric utility T&D industry. It is also suitable for those who seek a comprehensive understanding of the technology and its applications in this sector.
SCADA Training Outline for Electric Utility T&D Systems
DAY ONE
Introduction to SCADA in Electric Utility T&D Systems
SCADA System Components for T&D Systems
SCADA Communication Technologies and Protocols for T&D Systems
SCADA Applications in Substations
Hands-on Exercise: Basic SCADA System Setup for T&D Applications
DAY TWO
SCADA Applications in Power Distribution Networks
SCADA Applications in Transmission Networks
SCADA Cybersecurity in Electric Utility T&D Systems
SCADA System Maintenance and Troubleshooting for T&D Systems
Case Studies and Lessons Learned
Hands-on Exercise: Advanced SCADA System Configuration for T&D Applications
COURSE TIMETABLE
Both days:
Start: 10:00 am Eastern Time
Finish: 4:00 pm Eastern Time