Electrical Energy
By R. W. Hurst, Editor

Electrical energy is the power derived from the movement of electrons through a conductor. It powers homes, industries, and modern technology. This form of energy can be generated from various sources, including fossil fuels, solar, wind, and hydroelectric systems.
What is Electrical Energy?
Electrical energy is the result of electric charge flow, used to perform work in countless applications across daily life and industry.
✅ Powers lighting, heating, and electronic devices across all sectors
✅ Generated by power plants from renewable and non-renewable sources
✅ Converted from and into other energy forms, like mechanical or thermal
Electrical Energy: The Fundamental Source of Power
An Electric charge is a property of certain subatomic particles (e.g., electrons and protons) which interacts with the electromagnetic field and causes attractive and repulsive forces between them. Electric charges give rise to one of the four fundamental forces of nature, and is a conserved property of matter that can be quantified. In this sense, the phrase "quantity of electricity" is used interchangeably with the phrases "charge of electricity" and "quantity of charge." There are two types of charge: we call one kind of charge positive and the other negative. Through experimentation, we find that like-charged objects repel and opposite-charged objects attract one another. Coulomb's law gives the magnitude of the force of attraction or repulsion. For a broader understanding, visit how electricity works to see how it is generated, transmitted, and used across power grids and homes.
How Electric Fields Transfer Energy Between Charges
Michael Faraday introduced the concept of the Electrical Energy field. The field force acts between two charges, in the same way that the gravitational field force acts between two masses. However, the electric field is a little bit different. Gravitational force depends on the masses of two bodies, whereas the electromagnetic force depends on the electric charges of two bodies. While gravity can only pull two masses together, the force can be attractive or repulsive. If both charges are of the same sign (e.g. both positive), there will be a repulsive force between the two. If the charges are opposite, an attractive force will exist between the two bodies (as seen in static electricity and kinetic energy). The magnitude of the force varies inversely with the square of the distance between the two bodies and is also proportional to the product of the unsigned magnitudes of the two charges. Discover how electrical load determines the demand placed on a system’s energy supply.
Electrical Energy and Voltage Explained
The electric potential difference between two points is defined as the work done per unit charge (against forces) in moving a positive point charge slowly from one point to another. Choose one point as a reference with zero potential. The electric potential at any other point equals the work required per unit charge to move a positive test charge from the reference point to that location. For isolated charges, the reference point is usually taken to be infinity. The potential is measured in volts. (1 volt = 1 joule/coulomb) The electric potential is analogous to temperature: there is a different potential at every point in space, and the potential gradient indicates the direction and magnitude of the driving force behind electric current flow. Similarly, there is an electric potential at every point in space, and its gradient indicates the direction and magnitude of the driving force behind the movement of charged energy. To understand how voltage influences electrical energy, it's essential to grasp how potential difference drives current through circuits.
Electric Current: Flow of Charge That Powers Technology
Current is a flow of electrical energy, and its intensity is measured in amperes. Examples of electric currents include metallic conduction, where electrons flow through a conductor such as a metal wire, and electrolysis, where ions (charged atoms) flow through liquids. The particles themselves often have energy to move quite slowly, while the moving electric field that drives them propagates at close to the speed of light. See energy conduction for more information. Alternating current and direct current each transfer electrical energy differently, depending on the application.
Devices that utilize charge flow principles in materials are referred to as electronic devices.
A direct current (DC) is a unidirectional flow, while an alternating current (AC) reverses direction repeatedly. The time average of an alternating current is zero, but its capability (RMS value) is not zero.
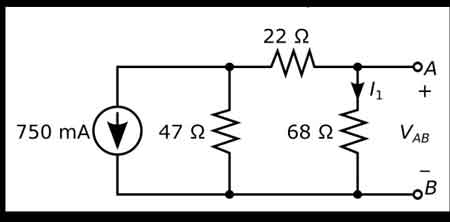
Ohm's Law is an important relationship describing the behaviour of energy, relating it to voltage. Explore the principles behind Ohm’s Law to see how voltage, current, and resistance interrelate in determining energy flow. Learn how electrical resistance affects energy loss and heat generation in systems.
For historical reasons, power is said to flow from the most positive part of a circuit to the most negative part. The current thus defined is referred to as conventional current. It is now known that, depending on the conditions, a current can consist of a flow of charged particles in either direction, or even in both directions at once. The positive-to-negative convention is widely used to simplify this situation. If another definition is used - for example, "electron current" - it should be explicitly stated.
Related Articles