Grounding System - Electrical Fault Protection
A grounding system provides a safe path for electrical current to dissipate into the earth, protecting people and equipment. It ensures voltage stability, enhances fault protection, and prevents shock hazards in homes, industrial sites, and power distribution networks.
What is a Grounding System?
A grounding system plays a crucial role in the safety and performance of electrical circuits and equipment. It protects against electrical faults, ensuring the smooth and efficient functioning of various electrical equipment.
✅ Provides a low-resistance path to safely discharge electrical faults into the earth
✅ Enhances system reliability by stabilizing voltage during normal and fault conditions
✅ Prevents shock hazards and protects people and equipment from electrical damage
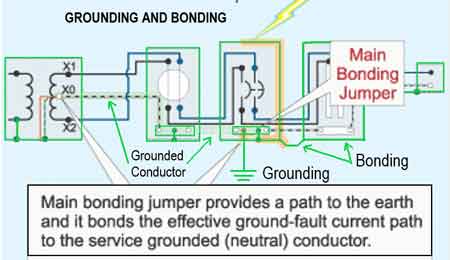
Grounding and Bonding and the NEC 250 Training
Electrical Grounding and the CE Code Training
Request a Free Power Quality Training Quotation
Electrical grounding, also known as earthing, establishes a direct link between the electrical equipment and the earth. This connection allows excess electrical energy to be safely dispersed into the ground, preventing damage to the equipment and reducing the risk of electrical fires or electrocution. Explore our main Power Quality and Grounding Channel to understand how earthing interacts with harmonics, load balancing, and power factor correction in modern electrical networks.
The electrical power network comprises various components, including a power supply, internal wiring, protective devices, and electrical equipment. A well-designed grounding system ensures that all these components work harmoniously and efficiently. One of the critical components is the equipment earthing conductor, which is responsible for connecting the non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical equipment to the grounded connection.
Ground fault protection is another essential aspect. When an electrical current strays from its intended path due to a fault in the system, such as a short circuit, the grounding system helps protect against potential hazards. The ground wire carries the excess current away from the electrical equipment, preventing overheating or fires. A comprehensive understanding of electrical grounding is essential for designing safe and code-compliant grounding systems in both residential and industrial applications.
High resistance grounding is a technique used in high-voltage networks to limit the fault current and reduce the risk of damage to electrical equipment. High-resistance earthing minimizes the impact of ground faults on the electrical system by connecting a resistor between the neutral point of the power supply and the grounded connection. To explore how grounding affects system performance, see our detailed guide on the electrical grounding code, including NEC and CSA standards.
Proper grounding of electric appliances is essential for protecting homes and facilities from hazards such as lightning strikes and electrical faults. By establishing a safe path for excess current, earthing not only safeguards equipment but also complies with safety standards. The National Electrical Code (NEC) outlines specific limits and requirements for grounding systems to ensure effective fault protection. Adhering to these guidelines helps prevent equipment damage and personal injury, while reducing the risk of non-compliance with the NEC. Ultimately, proper grounding plays a key role in reducing the impact of lightning strikes and ensuring electric appliances operate safely within NEC limits.
National Electric Code (NEC) and Grounding and Bonding
The National Electric Code (NEC) and National Electrical Code are regulatory standards that govern electrical equipment's design, installation, and maintenance. These codes ensure that equipment complies with safety regulations and provides a safe environment for the occupants of a building.
The power supply is the source of electrical energy for equipment. A well-designed grounding system helps maintain the stability of the power supply, preventing voltage fluctuations and safeguarding electrical equipment from damage. It also ensures the power supply operates efficiently, minimizing energy loss and reducing operational costs.
Protective devices, such as circuit breakers and fuses, are essential components of an electrical system that safeguard equipment and users from electrical hazards. It works with these protective devices, ensuring they function correctly in the event of a fault. When a ground fault occurs, the protective devices disconnect the power supply, preventing further damage to the equipment and reducing the risk of injury to users.
Resistance grounded systems are a type designed to limit the fault current and minimize the impact of ground faults on the electrical network. By connecting a resistor between the neutral point of the power supply and the grounded connection, resistance grounded systems help protect electrical equipment and maintain power stability. Learn how proper bonding techniques support your earthing strategy by visiting our page on grounding and bonding for fault current control and voltage stabilization.
Short Circuit Protection and Grounding
Short circuit protection is another crucial aspect of a grounding system. A short circuit works with protective devices to quickly disconnect the power supply, preventing damage to electrical equipment and reducing the risk of electrical fires or electrocution.
High and low-voltage systems require different earthing techniques to ensure their safety and performance. Therefore, it should be designed according to the voltage system's specific requirements, considering fault current levels, power stability, and equipment protection. If you're working on specifying equipment, our overview of the grounding electrode conductor explains its role in connecting system components to earth ground.
A well-designed system is essential for the safety and performance of electrical circuits and equipment. By incorporating earthing into electrical power systems, the risk of electrical hazards, such as fires and electrocution, can be significantly reduced. In addition, adhering to the National Electric Code (NEC) and National Electrical Code regulations ensures that equipment complies with safety standards, providing a secure environment for users and safeguarding valuable electrical equipment.
Related Pages
On-Site Training
Interested in cost effective, professional on-site electrical training?
We can present an Electrical Training Course to your electrical engineering and maintenance staff, on your premises, tailored to your specific equipment and requirements. Click on the link below to request a Free quotation.
EF PARTNER MEDIA
Product Showcases
Shared Media
















