Step Down Transformers
By R.W. Hurst, Editor
Substation Maintenance Training
Our customized live online or in‑person group training can be delivered to your staff at your location.

- Live Online
- 12 hours Instructor-led
- Group Training Available
Download Our OSHA 4474 Fact Sheet – Establishing Boundaries Around Arc Flash Hazards

- Understand the difference between arc flash and electric shock boundaries
- Learn who may cross each boundary and under what conditions
- Apply voltage-based rules for safer approach distances
Step down transformers reduce high voltage to a lower, safer level for residential, commercial, or industrial use. These devices are essential in power distribution systems, converting voltage efficiently and safely for use in low-voltage equipment.
What are Step Down Transformers?
Step down transformers are electrical devices that reduce the voltage level of an AC power supply.
✅ Converts high voltage to usable lower voltage for equipment
✅ Ensures electrical safety in homes, businesses, and factories
✅ Integral to efficient power distribution systems
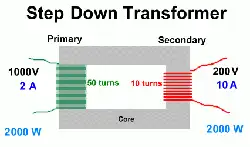
Step down transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, utilizing two or more coils of wire (windings) wound around a common magnetic core. A step-down transformer reduces high voltage to safer levels, making it ideal for residential and commercial electrical systems.
Step down transformers are a type of power supply transformer designed for efficient voltage reduction, converting high input voltages down to lower, usable levels. It operates through electromagnetic induction between its primary and secondary windings, enabling safe and stable AC-to-AC conversion without altering the frequency. This type of transformer is essential in many transformer applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial systems, where lower voltages are required for safe equipment operation.
Step down transformers: Key Specifications and Applications
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Function | Reduces high voltage to lower, safer voltage levels |
| Voltage Direction | From high (primary winding) to low (secondary winding) |
| Current Direction | Increases current as voltage decreases (power remains approximately constant) |
| Typical Input Voltage | 240V, 480V, 13.8kV, etc. (depending on application) |
| Typical Output Voltage | 120V, 24V, 12V for residential or control circuit applications |
| Primary and Secondary Winding | Primary receives input power; secondary delivers reduced output power |
| Power Supply Type | AC to AC conversion |
| Common Applications | Homes, commercial buildings, control panels, power tools, HVAC systems |
| Advantages | Improved safety, equipment protection, efficient energy use |
How Do They Work?
They operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They consist of primary and secondary windings wrapped around a magnetic core. When AC power flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field in the core. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding. Since the primary winding has more turns than the secondary winding, the transformer converts the high voltage on the primary side down to a lower voltage on the secondary side, effectively stepping down the voltage level. For a deeper understanding of how voltage is modified in a system, see our explanation of what is a transformer?
Electricity Today T&D Magazine Subscribe for FREE

- Timely insights from industry experts
- Practical solutions T&D engineers
- Free access to every issue
In contrast to step-down devices, a step-up transformer increases voltage, and both types play crucial roles in power transmission.
Step Down Transformers: Common Applications
They are widely used in various applications:
-
Residential Power Supply: They convert high voltage from power lines down to the standard voltage level used in homes, typically 120V or 240V, ensuring safe and efficient power supply for household appliances.
-
Commercial and Industrial Equipment: They supply appropriate voltage levels for machinery, tools, and other equipment, which often require lower voltages than the transmission lines provide.
-
Electronics: They are used in devices such as chargers and adapters to convert a higher AC voltage to a suitable level for electronic gadgets.
Learn how single-phase transformers operate in household power distribution and how they compare to three-phase systems.
Choosing the Right Step-Down Transformer
Selecting the appropriate step-down transformer involves considering several key factors:
-
Voltage Requirements: Determine the input and output voltage levels needed for your application. Ensure the transformer's voltage ratings match these requirements.
-
Power Rating: Assess the power supply needed by your devices or equipment. They have power ratings typically measured in VA (volt-amperes) or kVA (kilovolt-amperes). Choose one that can handle the load.
-
Single Phase vs. Three Phase: Depending on your application, choose between single-phase or three-phase devices. Single-phase devices are commonly used in residential settings, whereas three-phase devices are typically employed in industrial applications.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the transformer meets local and international safety standards and regulations.
Our power transformers guide examines how various transformer types contribute to the grid's stability.
Safety Concerns
Safety is paramount when working with electricity. Always ensure the step-down transformer is properly grounded to prevent electrical shocks. Use appropriate fuses or circuit breakers to protect the transformer and connected circuits from overloads.
-
Proper Installation: Ensure the transformer is installed by a qualified electrician following all safety guidelines.
-
Overloading: Avoid exceeding the transformer's rated capacity, as this can lead to overheating and potential failure.
-
Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect and maintain the transformer to ensure it operates safely and efficiently.
-
Grounding: Proper grounding is essential to prevent electrical shocks and ensure safe operation.
Understand how transformer load and safety are managed by reviewing our transformer grounding diagram.
Voltage Conversion for International Travel
Yes, step down transformers can convert voltage from one country's standard to another, making them useful for travellers and expatriates. For example, a step-down transformer can convert 240V AC power (common in Europe) to 120V AC (common in the United States). When selecting a transformer for this purpose, ensure it meets the voltage and frequency standards of both countries and has the appropriate power rating for the devices you plan to use.
Step down transformers are indispensable devices that bridge the gap between high voltage transmission and safe, usable electricity for our everyday lives. By understanding their working principles and considering the key factors when selecting and using them, we can harness their power to ensure efficient and safe electrical power utilization in our homes and businesses.
Explore the many types, including dry-type and isolation models, each suited for specific electrical applications.
Related Articles