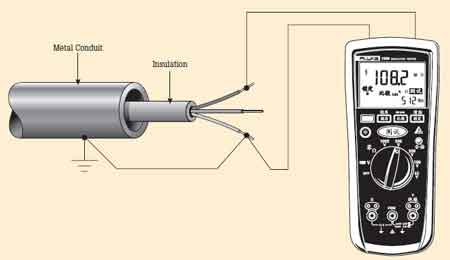
Arc Flash

NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace sets arc flash and shock protection requirements, PPE categories, lockout/tagout, risk assessment, approach boundaries, incident energy analysis, training, and OSHA-aligned safe work practices.
What Is the NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace?
NFPA 70E defines arc flash/shock controls, PPE, LOTO, and procedures to reduce electrical risk for workers.
✅ Arc flash risk assessment and incident energy analysis
✅ Shock boundaries, PPE categories, and approach limits
✅ LOTO procedures, energized work permits, and training
The NFPA 70E Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace is essential to workplace safety, especially in industries where workers are exposed to electrical equipment and hazards. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 70E standard is a vital document that provides safety requirements for electrical workers to protect them from electrical hazards. For a concise overview of scope and intent, consult what is NFPA 70E to understand foundational concepts.
Following the NFPA 70E standard is critical for ensuring safety in the workplace. By implementing the safety practices outlined in the standard, employers can protect their workers from hazardous energy levels and therefore reduce the risk of electrical incidents and injuries. For broader context on implementation and compliance, see NFPA 70E resources that outline common best practices.
What is the NFPA 70E Arc Flash Standard?
The NFPA 70E is a standard for electrical safety in the workplace that provides safety requirements for electrical workers to reduce exposure to electrical hazards. The standard was first introduced in 1979 and has since been updated to reflect current safety practices and technology. The purpose of the NFPA 70E standard is to protect workers from electrical hazards and reduce the risk of electrical incidents and injuries.
The NFPA 70E standard outlines safety procedures for electrical workers when working on or near electrical equipment. It covers various safety topics, including training, program development, hazard analysis, equipment labelling, personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response. For a high-level chapter-by-chapter breakdown, refer to an NFPA 70E chapter summary to align policies and training.
What Does NFPA 70E Require Regarding Safety-Related Work Practices?
The NFPA 70E standard, associated with the National Electrical Code, requires employers to develop and implement safety-related work practices to protect workers from electrical hazards. These practices include: A detailed overview of employer and worker obligations is compiled in NFPA 70E arc flash requirements to support program development.
Training: The standard requires employers to provide training for workers exposed to electrical hazards. The training should cover arc flash and shock protection principles, hazard recognition, and safe work practices.
Hazard Analysis: Employers must conduct a hazard analysis to identify electrical hazards and assess the risk of electrical incidents. The hazard analysis should include an evaluation of the electrical system, equipment, and tasks performed by workers.
Equipment Labeling: Electrical equipment must be labelled to identify its voltage, current, and other electrical characteristics. The labelling should also indicate the appropriate PPE required for safe work practices.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): The NFPA 70E standard requires employers to provide appropriate PPE for workers exposed to electrical hazards. The PPE should be selected based on the hazard analysis and include arc-rated clothing, gloves, and face shields.
Lockout/Tagout: The standard requires employers to establish a lockout/tagout program to prevent the accidental release of hazardous energy during electrical equipment maintenance and repair.
Emergency Response: Employers must develop an emergency response plan for electrical incidents and injuries. The plan should include procedures for administering first aid, evacuating the area, and contacting emergency services.
What is the Most Current NFPA 70E Edition?
The most current edition of the NFPA 70E standard is the 2021 edition. This edition includes several significant changes that affect electrical safety practices in the workplace. For a quick recap of key revisions and emphasis areas, review the NFPA 70E 2021 edition summary before updating procedures.
One of the major changes in the 2021 edition is the introduction of the Hierarchy of Risk Controls. This hierarchy provides a framework for safe work practices by prioritizing risk control measures based on their effectiveness. The Hierarchy of Risk Controls includes the following five levels:
Elimination: Eliminating the hazard by de-energizing the equipment or removing the hazard altogether.
Substitution: Replacing the hazard with a less hazardous alternative.
Engineering Controls: Using engineering controls to mitigate the hazard, such as barriers, insulation, and ventilation.
Administrative Controls: Implementing administrative controls, such as training and work procedures, to reduce the risk of exposure to the hazard.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Using PPE as a last line of defence to protect workers from hazards that other means cannot eliminate or control.
Organizations planning ahead can preview anticipated updates in the NFPA 70E 2024 update to prepare for future alignment.
Significant Changes To The NFPA 70E 2021 Edition
Another significant change in the 2021 edition is modifying the Incident Energy Analysis method. This method is used to calculate the incident energy exposure of a worker in an arc flash hazard. The modification includes using a unified set of calculation equations to provide more accurate results and simplify the calculation process.
The 2021 edition also includes updates to the PPE requirements, including adding a new type of PPE known as an "arc-rated face shield." This PPE is designed to protect the face and neck of workers from the thermal hazards of an arc flash.
In addition to these changes, the 2021 edition of the NFPA 70E standard includes several other updates and clarifications that reflect current industry best practices and technology. Therefore, employers and workers must stay up-to-date with the latest standard edition to ensure they follow current work practices. For day-to-day application, NFPA 70E practical guidance can help translate requirements into effective field practices.
Related Articles
Download Our FREE Arc Flash Handbook

Our Electrical Safety and Arc Flash Handbook Volume 11 is the most popular handbook in our handbook series.
Our latest Arc Flash and Electrical Safety Handbook Volume 11 is a valuable source of information for electrical professionals working in Industrial, Commercial and Institutional power systems who are exposed to the risk of arc flash accidents, which can cause serious injury and death.
This 96-page FREE to download handbook examines important electrical safety issues faced by front line electrical workers.
Table of Contents
CHAPTER ONE - Arc Flash And Blast
CHAPTER TWO - Arc Flash Codes And Standards
CHAPTER THREE - Arc Flash In The Workplace
CHAPTER FOUR - Electrical Safety Procedures
CHAPTER FIVE - Lockout Tagout
CHAPTER SIX - Arc Flash PPE
CHAPTER SEVEN - Arc Flash Training
CHAPTER EIGHT - Arc Flash Anaylsis
CHAPTER NINE - Arc Flash Consulting
Download Today!
Latest Arc Flash Articles

Lockout Tagout Devices
Lockout tagout devices secure hazardous energy sources during maintenance, preventing accidental startup. These OSHA- and NFPA 70E-compliant safety tools include padlocks, tags, hasps, and circuit breakers for effective worker protection.
What are Lockout tagout devices?
Lockout tagout devices are tools designed to isolate energy sources and protect workers during maintenance. They:
✅ Prevent accidental machine startup and energy release
✅ Ensure OSHA and NFPA 70E compliance with proper isolation
✅ Include padlocks, tags, hasps, breaker locks, and valve covers
Request a Free Training Quotation
Why LOTO Devices Matter
They are more than just compliance tools—they are essential safeguards that protect workers from life-threatening injuries. By physically isolating energy sources, these lockout tagout devices eliminate the risk of accidental startup during servicing. They also ensure compliance with OSHA and NFPA 70E standards, helping employers avoid costly fines and liability. Beyond safety, effective lockout tagout practices reduce equipment downtime, minimize accidents, and build a culture of trust where employees know their well-being is prioritized.
Training and Compliance
Workers can gain essential skills through OSHA Lockout Tagout Training, designed to meet federal safety expectations. Proper training ensures that employees understand how to select and apply LOTO devices, recognize hazardous energy sources, and follow OSHA and NFPA 70E requirements. Training also helps employers maintain compliance, reduce the risk of costly violations, and foster a safer and more efficient workplace.
They are essential for controlling hazardous energy during the maintenance or servicing of machines and equipment. These devices are applied to energy-isolating devices—such as disconnect switches, valves, or plugs—to ensure that machinery cannot be inadvertently energized, preventing serious injuries or fatalities. Understanding the various types of devices, their applications, and OSHA requirements is crucial for developing a compliant and effective LOTO program. If you’re new to the concept, see What is Lockout Tagout? to understand the fundamentals and how they apply in industry.
To meet the requirements outlined in CFR 1910.147, employers must implement lockout tagout practices using devices that prevent the unexpected startup of machines during servicing. This includes securing not only primary energy isolating mechanisms but also secondary controls, such as a push button that could accidentally energize equipment. A wide range of lockout tagout devices is available to accommodate different equipment types and control configurations, ensuring that facilities can tailor their energy control strategies to match specific operational needs. Compliance depends on knowing the OSHA Lockout Tagout Standard, which defines the rules for hazardous energy control.
Lockout Devices vs Tagout Devices
While both are used to prevent the unexpected startup or release of stored energy, they serve different functions and offer varying levels of protection:
-
Lockout Devices are physical restraints—typically padlocks or mechanical attachments—that hold an energy isolating device in a safe or "off" position. They provide a positive means of securing energy isolation.
-
Lockout Tagout Devices are warning labels or signs attached to energy-isolating devices. While they don’t provide physical restraint, they communicate that the equipment must not be operated. OSHA allows tagout alone only when an energy isolation method is not feasible and when additional safety measures are in place.
Whenever possible, OSHA mandates that lockout is preferred over tagout because it provides a more secure form of energy control. A closer look at OSHA Lockout Tagout Requirements reveals the specific steps employers must follow for compliance.
Types of Lockout Tagout Devices
There is no one-size-fits-all device. Each type is designed for specific energy control points and must be selected based on the nature of the equipment and the energy involved. Every facility needs a documented Lockout Tagout Program to integrate policy, procedures, and training into daily operations.
1. Electrical Plug Locks
Used to cover and secure electrical plugs on portable equipment. These devices prevent the plug from being reinserted into the outlet during servicing.
2. Circuit Breaker Locks
These are applied directly to circuit breakers, preventing them from being switched back to the "on" position. Models vary depending on the type of breaker and the manufacturer.
3. Valve Locks
-
Ball Valve Lockouts: Encase the valve handle to prevent rotation.
-
Gate Valve Lockouts: Fit over the valve wheel and are usually adjustable by diameter.
-
Butterfly Valve Lockouts: Clamp the valve handle in place to prevent movement.
4. Pneumatic Locks
Used on air compressor lines to block airflow. These devices typically clamp directly to the air hose connection or the fitting.
5. Plug and Cord
Enclose power cords or plugs to block access. This is useful in environments where machinery is powered by a simple power cord.
6. Group Lockout Boxes
These allow multiple workers to apply their personal locks to a central box holding the primary lockout key. It ensures that no single worker can re-energize the equipment until all locks are removed. When several employees are involved, Group Lockout Tagout provides a method to protect everyone working on shared equipment.
7. Lockout Hasps
These metal loops enable multiple padlocks to be applied to a single isolation point, a common feature in team-based maintenance scenarios.
8. Tagout Devices
OSHA-compliant warning tags that identify the authorized worker, date, and purpose of the machine lock. Tags must be durable, securely fastened, and legible.
Choosing the Right Device for the Job
Selecting the correct lockout device depends on the type of hazardous energy present and the energy isolating mechanism used. A proper match ensures effectiveness and compliance.
-
For electrical panels, circuit breaker safety locks are essential.
-
For compressed air systems, pneumatic safety locks or plug safety locks are appropriate.
-
Choosing between ball, gate, or butterfly valve safety locks for valves depends on the type of valve and its handle configuration.
When unsure, refer to the equipment manufacturer’s documentation or conduct a hazard assessment. OSHA mandates that lockout tagout devices must be standardized, durable, and substantial enough to prevent accidental removal. Step-by-step guidance is covered in our Lockout Tagout Procedure, outlining how to properly shut down, isolate, and secure equipment.
Examples of Correct and Incorrect Applications
- Correct: Use a gate valve safety lock that completely covers the handwheel and apply a padlock through its designated latch point.
- Incorrect: Placing a tag on a valve without any physical restraint when a lockout tagout device could have been applied.
Improper device use can lead to OSHA violations and, more importantly, create unsafe conditions for workers. Therefore, it’s essential to train authorized employees on proper device selection and use.
LOTO devices are more than safety accessories—they’re essential tools for preventing unintended energy releases. Selecting and applying the right device for each energy isolating point is central to LOTO effectiveness. By understanding the types of hazardous energy and choosing compliant, task-specific equipment, employers can meet OSHA standards while protecting workers from harm.
For a full overview of the topic, start with our Lockout Tagout guide, which explains why energy control is critical for workplace safety.
To clear up common issues, explore Lockout Tagout Questions, where frequently asked topics are explained in detail.
Related Articles
-
To clear up common issues, explore Lockout Tagout Questions, where frequently asked topics are explained in detail.
To ensure compliance and worker protection, The Electricity Forum offers specialized Construction Electrical Safety Training, including NFPA 70E Training and CSA Z462 Arc Flash Training courses. Request a free training quotation today to equip your team with the knowledge and skills they need to stay safe on the job.

Arc Flash PPE Requirements for NFPA 70E Compliance
Arc flash PPE requirements ensure workers wear appropriate protective gear, like arc-rated clothing and face shields, based on incident energy levels, minimizing injury risks.
What are Arc Flash PPE Requirements?
Arc flash PPE requirements are safety standards mandating specific protective equipment, such as arc-rated clothing, gloves, and face shields, based on the calculated incident energy exposure during electrical tasks, ensuring worker safety from arc flash hazards.
-
✅ Four PPE Categories: Classified by incident energy levels (4 to 40+ cal/cm²), each category dictates specific protective gear requirements.
-
✅ Determination Methods: PPE needs are identified through either detailed incident energy analysis or standardized task-based tables.
-
✅ Compliance Standards: Following NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 ensures proper PPE selection and enhances electrical safety.
Arc flash PPE requirements define the essential safety measures electrical workers must follow when performing energized tasks. From identifying hazard levels to selecting properly arc-rated (AR) gear, compliance with NFPA 70E guidelines ensures that the right protective clothing is worn for every situation. These standards help prevent serious injuries by aligning personal protective equipment (PPE) with the specific risks present in industrial and commercial electrical systems.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Selecting the right arc flash protection starts with understanding and following electrical PPE guidelines based on a thorough incident energy assessment of the work environment. This assessment helps determine the potential thermal energy a worker may be exposed to during an arc flash event. Based on this, employers must align task-based protection levels with the appropriate PPE hazard classification, ensuring that each job matches the correct safety equipment level. Organizations can minimize risk by identifying the required protective gear by task while meeting compliance requirements and safeguarding workers from preventable injuries. Use this arc flash PPE requirements chart to match clothing and gear with incident energy levels.
Understanding Hazards and PPE Levels
An arc flash is a dangerous electrical event that can release a violent burst of heat and pressure, causing severe injuries, burns, or even fatalities. To protect against this, NFPA 70E outlines four PPE levels based on incident energy, measured in cal/cm². Each level requires AR clothing and accessories designed to withstand a certain degree of thermal exposure.
PPE categories are based on the incident energy levels likely to be encountered during a task:
-
Category 1 (4 cal/cm²): Requires AR shirt and pants or coverall, face shield with wrap-around protection, hard hat, and voltage-rated gloves.
-
Category 2 (8 cal/cm²): This category adds an AR balaclava or flash hood and may require a heavier fabric weight.
-
Category 3 (25 cal/cm²): Requires a full suit, AR hood, gloves, and hearing protection.
-
Category 4 (40 cal/cm²): This category involves multi-layered suits designed for the highest exposure levels. For severe hazard scenarios, read about high-calorie suits on our 100 Cal Arc Flash Suit page.
Understanding the standards for minimum ratings ensures that protection is properly aligned with the electrical hazard classification for the task at hand. To better understand the different protection levels, explore our Arc Flash PPE Category page, which breaks down hazard levels and required gear. The NFPA 70E PPE requirements help define the proper protective equipment for various electrical tasks.
How Arc Flash PPE Requirements Are Determined
There are two acceptable methods under NFPA compliance for determining what PPE is required:
-
Incident Energy Analysis: A detailed engineering assessment calculates thermal energy at working distance. This method provides exact values for incident energy exposure levels and drives specific PPE requirements.
-
PPE Category Tables: Table 130.7(C)(15) and related charts define the PPE required for various tasks and equipment types, providing a simplified way to assess risk when a full engineering analysis is not performed.
Both approaches are valid and should be used according to the system's complexity and the precision needed for task-specific PPE.Selecting the right arc flash clothing is essential for compliance with NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 standards.
Key Electrical Safety Requirements
In addition to wearing the correct PPE, electrical workers must follow these requirements to ensure safety and legal compliance:
-
PPE must be AR and tested to meet or exceed the task's energy exposure.
-
Garments must be inspected and maintained regularly for damage, contamination, or wear that could reduce protection.
-
PPE must provide full body coverage, leaving no skin exposed during the task.
-
PPE should be clearly labeled with ratings in cal/cm².
-
Training must be provided to workers on the correct use and limitations of their PPE.
Employers are also responsible for maintaining a documented PPE selection process to ensure workers are properly outfitted based on the risk and job type. Explore the full range of arc flash safety gear required to minimize injuries from electrical incidents.
Best Practices for PPE Implementation
To meet and exceed requirements, companies should:
-
Integrate PPE selection into job safety planning.
-
Use risk-based PPE assessment tools when possible.
-
Maintain and audit PPE inventories to ensure availability and compliance.
-
Train staff regularly on PPE care, storage, and donning procedures.
In high-risk environments, incident energy suits and thermal-resistant garments offer additional protection, especially for workers operating close to energized components. Learn what goes into a fully compliant suit by checking out our in-depth page on the Arc Flash Suit, including face shields, gloves, and head protection. Learn how PPE performance is evaluated and rated for arc flash protection to ensure worker safety in high-risk environments.
Arc flash PPE requirements are not static checklists—they are living standards that evolve with each update of NFPA 70E. Organizations create a safer and more compliant electrical work environment by following proper PPE selection guidelines, understanding electrical hazard levels, and enforcing correct usage policies. Proper application of these rules not only satisfies compliance—it saves lives. Arc Flash Category 1 PPE includes basic protective clothing for tasks with low incident energy exposure.
Related Articles:
Explore our Arc Flash Training Programs or contact us to Request a Free Training Quotation for group safety sessions and PPE consultation.

Electrical Safety Work Explained
Electrical safety work ensures risk assessment, lockout-tagout, arc-flash boundaries, PPE, grounding, and isolation procedures for switchgear and panels, meeting NFPA 70E and OSHA standards to protect technicians during maintenance, testing, and commissioning.
What Is Electrical Safety Work?
Electrical safety work defines procedures to control electrical hazards during installation, testing, and maintenance.
✅ Perform arc-flash risk assessment and establish approach boundaries
✅ Apply lockout-tagout, verify isolation, and live-dead-live testing
✅ Use rated PPE, insulated tools, and test-before-touch protocols
Electrical safety work is critical for protecting personnel and equipment in industrial and commercial environments with high voltage and electrical hazards. From arc flash risks to shock and burn injuries, working with or around energized systems demands strict adherence to safety protocols. This includes proper training, personal protective equipment (PPE) use, and compliance with standards like NFPA 70E and CSA Z462. Implementing robust electrical safety procedures helps prevent workplace accidents and fatalities and ensures regulatory compliance, operational reliability, and peace of mind for employers and workers alike. For a broader overview of policies and controls, the Electricity Forum’s guide on electrical safety in the workplace explains program elements and common hazards.
Comprehensive arc flash instruction is further outlined in arc flash safety training resources that clarify risk assessment steps and PPE selection.
To understand compliance obligations and curriculum depth, review the detailed arc flash training requirements that many organizations align with.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Organizations planning programs can map competencies using this overview of electrical safety training topics before tailoring courses to their workforce.
Workers employed in the electrical field are expected to be very knowledgeable in how to work safely. In Canada, the Electrical Safety Authority (ESA) is one such body that offers tips and guidelines for novice electricians and ordinary laypersons while also being the monitoring body for licensed contractors and electricians. For construction environments, practical checklists in construction electrical safety address site-specific controls and coordination with other trades.
Key tips for working with basic electricity:
- Know the relevant electrical safety code for their province and municipality
- Try to work in a de-energized environment, ensuring the power is off and double-checking with a tester
- Use only approved products, identifiable by the mark of a recognized certification agency (Underwriters Laboratories, UL)
- Always have your work inspected as required by the electrical safety code
In the United States, it is the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), a government agency of the Department of Labor responsible for maintaining a safe work environment. Electrical safety is just one aspect of OSHA’s many requirements for worker safety. Anyone who may come into contact with live electricity or an electrical hazard must be trained in electrical safety. OSHA has set forth regulations on the minimum training a worker must have, whether in a classroom or through on-the-job training. To meet these expectations, organizations can reference consolidated electrical safety requirements that translate regulatory language into actionable controls.
Electrical workers must be trained to work safely around de-energized and energized equipment. They must know lockout/tagout procedures for detaching a piece of equipment from its power source, and securing the power source so that it does not become re-energized. A general rule of thumb for working on energized parts is to allow contact up to less than 50 volts. In production settings, proven practices from industrial electrical safety help teams balance uptime with hazard mitigation.
Another part of training includes properly using and caring for portable electrical equipment such as extension cords. Workers must be trained to inspect the equipment for damage visually and connect the equipment to a power source properly.
Employees working around electricity must be trained in the type and proper use of protective equipment (PPE – Personal Protective Equipment). They must know how to use insulated headgear and eye protection in appropriate settings where there is a danger to the head or eyes. Employees must be able to determine when insulated tools should be used (such as working around or on an exposed electrical circuit). Employees who must be trained in electrical safety but are not qualified personnel (unqualified personnel) must also be trained in other electrical safety practices that will keep them safe. Unqualified persons are deemed those not permitted to work on or near exposed live electricity.
Qualified personnel must be trained in how to locate and identify exposed live electrical circuits and equipment. Training must include determining the voltage of these live parts and accurately knowing the distance that voltage can travel through the air.
Related Articles
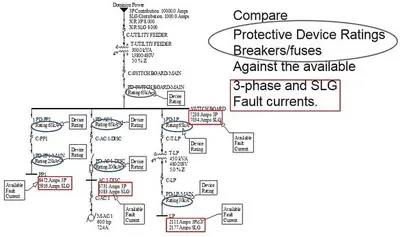
Incident Energy Explained
Incident energy is the heat released during an arc flash, measured in cal/cm². It defines arc flash boundaries, sets PPE levels, and ensures NFPA 70E compliance. Reducing incident energy lowers burn risk, improves safety, and supports safe electrical practices.
What is Incident Energy?
Incident energy is a critical metric used to measure the thermal energy released during an arc flash incident, expressed in calories per square centimetre (cal/cm²).
✅ Measures arc flash thermal energy in cal/cm²
✅ Determines proper PPE level and arc flash protection boundaries
✅ Used in NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 arc flash studies and risk assessments
Request a Free Training Quotation
This value determines the appropriate level of personal protective equipment (PPE) required to prevent serious injuries such as second- and third-degree burns. Accurate calculations of incident energy exposure are the foundation of any effective arc flash safety program, enabling employers to establish arc flash boundaries, apply compliant warning labels, and enforce safe work practices.
A reliable arc flash study must include an incident energy evaluation to ensure worker safety and compliance with both NFPA 70E and CSA Z462 standards. For step-by-step calculations and case studies, check our incident energy analysis page.
Why Incident Energy Matters
Arc flash incidents are among the most dangerous electrical hazards. Thousands of incidents occur annually, causing hundreds of serious injuries and fatalities. Beyond personal harm, arc flash events lead to costly downtime, equipment loss, and legal liability.
By defining incident energy, safety professionals can:
-
Protect workers from severe burns.
-
Ensure compliance with NFPA 70E and CSA Z462.
-
Reduce insurance costs and operational risk.
Understanding and applying these principles is crucial for creating safer workplaces.
Arc flash incidents pose a serious threat to electrical workers, often resulting in severe arc flash injuries such as second- and third-degree burns.
Within this arc flash boundary, the use of personal protective equipment PPE is not optional—it’s essential.
See our Arc Flash PPE article for more information.
Implementing effective OSHA electrical safety protocols starts with conducting a formal hazard analysis that considers system voltage, fault current, and clearing time.
How Incident Energy Is Calculated Using IEEE 1584
To determine the amount of incident energy that can be released during an arc flash, electrical professionals rely on the IEEE 1584-2018 standard. This calculation takes into account a range of system and environmental variables.
Accurate assessment depends on understanding the following core inputs:
-
Arcing Current: The actual current that sustains the arc during the fault event.
-
System Voltage: The operating voltage of the equipment under evaluation.
-
Available Fault Current: The maximum short-circuit current supplied to the arc.
-
Clearing Time: How quickly protective devices interrupt the fault.
-
Working Distance: The distance between the arc and the worker, typically 18 inches.
These calculations are essential components of a full arc flash risk assessment and are often conducted using specialized software and data from the facility’s arc flash study (short circuit and coordination studies).
Real-World Example: How Incident Energy Affects PPE
Consider a 480V system with a potential fault current of 30,000 amps. Using IEEE 1584, the resulting incident energy may reach 9.6 cal/cm² at 18 inches.
At this level:
-
Workers require arc-rated clothing with an ATPV rating greater than or equal to the calculated exposure (≥12 cal/cm²).
-
If clearing time is reduced, incident energy may drop below 8 cal/cm², lowering PPE requirements and improving mobility.
For a deeper understanding of how these figures are determined, please refer to our main Arc Flash Study page.
Techniques to Reduce Incident Energy
Modern facilities use design and operational strategies to lower exposure:
-
Current-Limiting Fuses: Interrupt arcs within milliseconds.
-
Arc-Resistant Equipment: Redirects blast energy away from personnel.
-
Maintenance Mode Switches: Shorten trip times during energized work.
-
Zone-Selective Interlocking (ZSI): Improves protective coordination.
NEC requirements (such as Sections 240.67 and 240.87) mandate the reduction of incident energy in certain equipment, reinforcing the importance of proactive design.
These techniques are covered in more depth in our guide to arc flash study requirements, which outlines everything employers must include in a safety study.
Compliance With NFPA 70E and CSA Z462
Both standards require incident energy evaluations as part of a complete electrical safety program. Compliance includes:
-
Labeling equipment with incident energy values or PPE categories.
-
Providing PPE based on calculated exposure.
-
Training workers to recognize and mitigate arc flash hazards.
Skipping these steps exposes companies to citations, liability, and preventable accidents.
For further guidance, see our Arc Flash Study, Arc Flash PPE, OSHA Electrical Safety, and Lockout Tagout (LOTO) resources.
Arc Flash Analysis Training
Companies that skip these steps risk citations, legal liability, and preventable injuries. Discover how to develop a compliant program with our arc flash analysis training courses designed for qualified personnel. A comprehensive electrical safety program should include regular arc flash assessments, incident energy calculations, PPE training, and strict adherence to NFPA 70E compliance standards.
Benefits of Accurate Incident Energy Evaluation
Accurate evaluation delivers:
-
Reduced risk of life-threatening burns.
-
Improved compliance and lower liability.
-
Safer, more efficient work practices.
-
Reduced downtime and insurance costs.
Incident energy isn’t just a number—it is a benchmark that shapes every aspect of electrical safety. To protect your team and comply with regulations, a full arc flash study that includes incident energy evaluation is essential.
If you're looking to build or update your safety program, start with a full arc flash study and make incident energy output a central part of your risk management strategy.
Explore More Arc Flash Topics
Explore our Arc Flash Training Programs or contact us to Request a Free Training Quotation for group safety sessions and PPE consultation.

Qualified Electrical Worker: Tasks Explained
A qualified electrical worker is trained, authorized, and competent to perform tasks on energized equipment. Their expertise ensures compliance, electrical safety, risk assessment, and adherence to NFPA 70E standards in industrial and utility environments.
Who is a Qualified Electrical Worker?
A qualified electrical worker is an individual with the training, skills, and authorization to safely perform power related tasks on energized systems. A qualified electrical worker must understand the hazards of energized equipment, including arc flash, which can cause severe injuries without proper training and protective measures.
✅ Demonstrates safety knowledge and hazard risk assessment
✅ Meets OSHA and NFPA 70E training requirements
✅ Authorized to work on or near energized power equipment
It is someone who has received specific training and demonstrated the ability to safely work on or near energized electric power equipment. They can identify hazards, determine system voltage, and apply proper safety procedures in accordance with NFPA 70E standards.
Request a Free Training Quotation
Their qualifications, as per industry standards such as NFPA 70E, enable them to assess and handle potential hazards in the workplace. The importance of distinguishing between qualified and unqualified individuals is crucial for maintaining workplace safety, ensuring the proper handling of equipment, and minimizing risks. These workers are familiar with practices that reduce risk and follow established procedures for safe work. Their training equips them with an understanding of the safe operation of equipment, as well as how to mitigate hazards, including arc flash hazards and shock protection. Compliance requires training in safe work practices, such as those outlined in NFPA 70E arc flash training, ensuring workers recognize risks and apply correct procedures.
Moreover, a qualified person must receive training on identifying energized electric power equipment and installations, ensuring they can assess the risks and protect themselves and others. Their expertise extends to understanding how to apply an electrical safety program in day-to-day tasks. OSHA standards like 29 CFR 1910.147 lockout/tagout are essential for qualified workers to control hazardous energy before performing maintenance or repair.
What training is required to become a qualified electrical worker?
To become a qualified individual, one must undergo comprehensive training and education. This training program typically includes learning how to safely handle energized equipment and installations, assessing the risks associated with arc flash hazards, and determining the nominal voltage of electric power systems. Training also involves recognizing when special precautions, such as shock protection, are necessary.
A key component of this training is understanding work practices that promote safety. These include proper procedures for dealing with equipment that may pose a danger and ensuring that workers can manage these tasks with minimal risk of injury. The training also ensures that they can identify safety hazards, work within a safety program, and apply safe work practices. Importantly, this training must align with industry standards such as NFPA 70E. When performing risk assessments, workers often reference arc flash analysis to determine boundaries, PPE needs, and system voltage hazards.
What tasks can a qualified electrical worker perform?
A qualified worker is permitted to perform tasks that involve energized equipment and installations. This includes maintenance, repair, and installation of such systems. Their work also encompasses troubleshooting and identifying potential shock hazards in equipment. Tasks like these require not only technical expertise but also the ability to identify and mitigate risks, such as arc flash hazards.
In addition to working directly with energized systems, these workers also take part in assessing the condition of equipment and ensuring that safety measures are in place. Whether dealing with installations or handling routine maintenance, they are trained to follow safe work practices and handle a wide range of tasks associated with their expertise. A 40 cal arc flash suit is an example of PPE required for certain high-energy tasks, and qualified workers must know when such protection is mandated.
What is the difference between a qualified electrical worker and an unqualified worker?
The difference between a qualified worker and an unqualified one lies in their training and ability to assess and handle potential hazards. A qualified person has received safety training to identify hazards such as arc flash and knows how to apply protective measures. Their role often involves working directly with energized equipment, which is not permitted for unqualified workers.
Unqualified workers lack the necessary training and skills required to safely handle these tasks. They may assist in non-technical areas but are restricted from performing any duties that involve energized systems or potential hazards. The distinction is critical to ensuring the safety of workers in environments where the operation of equipment carries inherent risks.
Why is it important to have a qualified electrical worker perform tasks?
Ensuring that individuals handle tasks involving energized systems is essential for maintaining workplace safety. These individuals have demonstrated the skills and knowledge necessary to identify risks and apply the necessary precautions, thereby minimizing the likelihood of accidents or injuries. Their understanding of safe work practices, shock protection, and arc flash hazards enables them to perform their duties without endangering themselves or others.
Employing qualified workers also ensures compliance with safety standards, including NFPA 70E, which mandates that only individuals with the proper training should handle such tasks. This not only protects the workers but also ensures that equipment is properly maintained and operated, preventing costly downtime and accidents.
In summary, qualified workers play an essential role in maintaining safety standards in environments that involve energized equipment. Their expertise, training, and ability to manage risks are crucial in ensuring that all tasks are performed safely and efficiently. These workers follow strict safety protocols, as outlined by their training programs, to mitigate risks and handle hazardous situations with care.
Related Resources

Electrical Safety Tips Prevention
Electrical safety tips help prevent shock, fire, and accidents by guiding safe use of electricity. Following protective practices with equipment, circuits, and wiring reduces the risk and ensures compliance with workplace and home safety regulations.
What are the Best Electrical Safety Tips?
Electrical safety tips are practical guidelines that protect people and equipment from hazards in power systems by promoting awareness, safe practices, and compliance with standards.
✅ Prevent electric shock, arc flash, and fire hazards
✅ Encourage safe tool use, wiring, and protective equipment
✅ Support compliance with NFPA, OSHA, and industry standards
Request a Free Training Quotation
Quick Electrical Safety Tips Checklist
Here are ten must-do practices to reduce electrical hazards:
-
Inspect wiring, outlets, and cords on a regular basis.
-
Test ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCIs) often.
-
Avoid overloading outlets or extension cords.
-
Use properly rated PPE for arc flash and shock protection.
-
Ensure appliances and systems are properly grounded.
-
Follow lockout/tagout (LOTO) procedures before maintenance.
-
Keep power panels accessible and labelled.
-
Replace damaged cords and connectors immediately.
-
Train employees on recognizing hazards and responding safely.
Common Hazards and Prevention
Shock and Contact Hazards
Electric shock is one of the most common risks associated with this activity. Effective shock protection methods include using GFCIs in damp areas, proper grounding, and clear labelling of energized parts. NFPA 70E defines approach boundaries, which specify the minimum distances to prevent accidental contact. These measures form the foundation of energy contact prevention in workplaces. Understanding the dangers of arc blasts and related arc flash injuries underscores the importance of consistent safety practices and proper training for all qualified power workers.
Fire Risks
Fires often result from overloaded circuits, faulty wiring, or poor equipment maintenance. Using properly rated breakers with overcurrent protection, along with periodic circuit breaker coordination studies, helps reduce the risk of overheating. Facilities should also verify short circuit protection to prevent dangerous fault currents from causing fires.
Arc Flash Safety
Arc flash is one of the most hazardous arc flash events, with temperatures exceeding 35,000°F and the potential to generate pressure waves and cause shrapnel. Risk assessments, as defined in NFPA 70E and CSA Z462, utilize hazard categories and incident energy tables to guide the selection of PPE. Every facility should conduct a formal risk assessment procedure that evaluates equipment, fault current, and protective device settings to ensure optimal safety. This process ensures the reduction of safety hazards and compliance with relevant standards. For more details on protective clothing, see our Arc Flash PPE Clothing guide.
Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCI)
GFCIs detect ground faults and cut power before shocks occur. Install them in kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. Testing them monthly is critical to ensure they provide reliable protection. Install GFCI protection in areas where water and electricity are in close proximity, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and outdoor outlets. Regularly test GFCIs to ensure they are functioning correctly.
Safely Using Power Cords and Extension Cords
Power cords and extension cords should be used cautiously. Always inspect cords for damage before use. Avoid overloading and never run cords under rugs or doorways. Good placement practices help prevent both tripping hazards and overheating.
Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance reduces the likelihood of failure. Inspections should include insulation resistance (IR) testing, thermal imaging, and continuity checks. Many facilities also perform arc flash assessment studies, which analyze hazards and recommend protective measures. These evaluations are crucial in determining safe working distances and ensuring that only qualified workers perform tasks near energized parts.
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO)
A critical part of safety is lockout/tagout; OSHA’s 29 CFR 1910.147 standard outlines the procedures required to control hazardous energy during maintenance. Before performing energized work, always perform Lockout Tagout:
-
Shut down equipment.
-
Isolate energy with lockout devices.
-
Tag equipment clearly.
-
Verify de-energization with voltage testing.
When work must be performed while the equipment is energized, an Energized Work Permit (EWP) is mandatory. This document ensures the task is reviewed, justified, and carried out with appropriate PPE and boundaries.
Adherence to Codes and Standards
Compliance with NFPA 70E, CSA Z462, and OSHA ensures safe approach distances, defined hazard categories, and PPE selection. Consult licensed professionals to verify that systems meet these codes and incorporate the latest best practices.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Workers exposed to arc flash hazards must use PPE appropriate to the job. This includes voltage-rated gloves, arc-rated clothing, insulated tools, and face shields. Proper PPE, combined with shock protection methods and procedural controls, significantly reduces risks.
Related Articles: