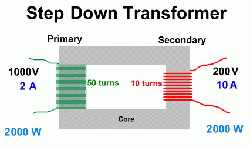
Step down transformers are a crucial component in many electrical systems, serving as a vital part in voltage conversion. They are designed to reduce the voltage level of an AC power supply, and operate through a process called electromagnetic induction.
At its core, step down transformers consist of two coils, the primary winding and the secondary winding, wrapped around a common core. The primary winding is the input side, where the high voltage is applied, while the secondary winding is the output side, where the voltage is reduced. It works by inducing a voltage in the secondary winding through the use of the primary winding.
One of the most critical features oin step down transformers is their turns ratio, which determines the relationship between the primary and secondary voltage levels. For instance, a core with a turns ratio of 1:2 would halve the voltage applied to the primary winding and output half the voltage to the secondary winding.
The turns ratio is determined by the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings. The greater the number of turns in the secondary winding, the lower the output voltage, while the fewer the turns in the primary winding, the higher the input voltage. By adjusting the turns ratio, it can step down the voltage to the required level.
One of the advantages is that it enables voltage conversion, which is essential in many electrical applications. For instance, electrical devices such as televisions, computers, and other appliances require a lower voltage than the power supplied to homes and buildings. Step down transformers can convert the high voltage supplied to homes and buildings into the lower voltage required for these devices to operate safely.
They can also be used to provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits. Electrical isolation is essential in situations where the circuits need to be protected from each other, such as in medical equipment or sensitive electronics.
There are different types available, including single-phase and three-phase step down transformers. Single-phase transformers are the most common type and are widely used in homes, buildings, and small businesses. Three-phase transformers, on the other hand, are used in large industrial settings where high voltage and current levels are required.
In addition to step down transformers, there are also step-up transformers that increase the voltage level. These operate in the opposite way to step down transformers, increasing the voltage level in the secondary winding compared to the primary winding.
When selecting a winding or core it is essential to consider the required input and output voltage levels, as well as the electrical load being supplied. It must be able to handle the required current levels without overheating or becoming damaged.
It is a critical component in many electrical systems, providing voltage conversion and electrical isolation. It works through electromagnetic induction and is designed to reduce the voltage level of an AC power supply. The turns ratio determines the voltage ratio between the primary and secondary windings, and different types of units are available for different applications. By selecting the right unit for the job, it is possible to achieve safe and efficient voltage conversion.
In addition to the turns ratio, another important factor to consider when selection is the electrical impedance. Electrical impedance refers to the resistance to the flow of electrical current. The impedance must be matched to the electrical load being supplied to ensure proper operation.
Another important feature is the voltage transformers ratio. This ratio describes the relationship between the input voltage and the output voltage. For example, a transformer with a voltage ratio of 10:1 would reduce the input voltage by a factor of 10, resulting in an output voltage one-tenth the size of the input voltage.
What is it used for?
It is used to reduce the voltage level of an AC power supply. It is commonly used in electrical systems to provide a lower voltage to electrical devices such as televisions, computers, and other appliances. It is also used to provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits.
How does it work?
It works through a process called electromagnetic induction. It consists of two coils, the primary winding and the secondary winding, wrapped around a common core. When an AC voltage is applied to the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The voltage induced in the secondary winding is proportional to the number of turns in the winding and the frequency of the AC power supply. By adjusting the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings, it can step down the voltage to the required level.
What is the difference between a step-up and a step down?
The main difference between step-up and step down transformers is the direction of the voltage conversion. A step-up model increases the voltage level, while a step down transformer reduces the voltage level. Both types of transformers work through electromagnetic induction and consist of two coils, the primary winding and the secondary winding, wrapped around a common core.
What are the advantages?
One of the main advantages of using it is that it enables voltage conversion, which is essential in many electrical applications. It allows high voltage supplied to homes and buildings to be converted into the lower voltage required for electrical devices to operate safely. Additionally, step down transformers can provide electrical isolation between the primary and secondary circuits, protecting sensitive electronics or medical equipment.
What are the different types?
There are different types, including single-phase and three-phase transformers. Single-phase transformers are the most common type and are widely used in homes, buildings, and small businesses. Three-phase transformers, on the other hand, are used in large industrial settings where high voltage and current levels are required.
How can I select the right step down transformer for my application?
When selecting a step down transformer, it is essential to consider the required input and output voltage levels, as well as the electrical load being supplied. Itmust be able to handle the required current levels without overheating or becoming damaged. Factors such as the turns ratio, voltage transformers ratio, and electrical impedance should also be considered. Consulting a professional electrical engineer can help ensure the right unit is selected for the specific application.
What safety precautions should I take?
When working with step down transformers, it is essential to take appropriate safety precautions to prevent electrical shock or other hazards. It should be installed and wired by a qualified electrician, and all electrical connections should be properly insulated. It should also be appropriately grounded to prevent electrical discharge. Additionally, it is essential to follow all safety guidelines and procedures when working with electricity, including wearing protective gear and avoiding contact with live circuits.